val zero : 'a nativeint
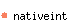
The native integer 0.
val one : 'a nativeint
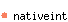
The native integer 1.
val minus_one : 'a nativeint
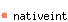
The native integer -1.
val neg : 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint
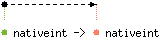
Unary negation.
val add : 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint

Addition.
val sub : 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint

Subtraction.
val mul : 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint

Multiplication.
val div : 'a nativeint ->
'b nativeint -{'c | Division_by_zero: 'c |}-> 'a nativeint
with 'b < 'a, 'c
'b nativeint -{'c | Division_by_zero: 'c |}-> 'a nativeint
with 'b < 'a, 'c

Integer division. Raise
Division_by_zero if the second
argument is zero. This division rounds the real quotient of
its arguments towards zero, as specified for Pervasives.(/).
val rem : 'a nativeint ->
'b nativeint -{'c | Division_by_zero: 'c |}-> 'a nativeint
with 'b < 'a, 'c
'b nativeint -{'c | Division_by_zero: 'c |}-> 'a nativeint
with 'b < 'a, 'c

Integer remainder.
val succ : 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint
Successor.
Nativeint.succ x is Nativeint.add x Nativeint.one.
val pred : 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint
Predecessor.
Nativeint.pred x is Nativeint.sub x Nativeint.one.
val abs : 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint
Return the absolute value of its argument.
val size : 'a int

The size in bits of a native integer. This is equal to
32
on a 32-bit platform and to 64 on a 64-bit platform.
val max_int : 'a nativeint
The greatest representable native integer,
either 231 - 1 on a 32-bit platform,
or 263 - 1 on a 64-bit platform.
val min_int : 'a nativeint
The greatest representable native integer,
either -231 on a 32-bit platform,
or -263 on a 64-bit platform.
val logand : 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint

Bitwise logical and.
val logor : 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint

Bitwise logical or.
val logxor : 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint

Bitwise logical exclusive or.
val lognot : 'a nativeint -> 'a nativeint
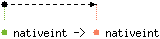
Bitwise logical negation
val shift_left : 'a nativeint -> 'a int -> 'a nativeint
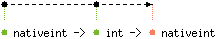
Nativeint.shift_left x y shifts x to the left by y bits.
The result is unspecified if y < 0 or y >= bitsize,
where bitsize is 32 on a 32-bit platform and
64 on a 64-bit platform.
val shift_right : 'a nativeint -> 'a int -> 'a nativeint
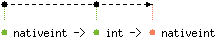
Nativeint.shift_right x y shifts x to the right by y bits.
This is an arithmetic shift: the sign bit of x is replicated
and inserted in the vacated bits.
The result is unspecified if y < 0 or y >= bitsize.
val shift_right_logical : 'a nativeint -> 'a int -> 'a nativeint
Nativeint.shift_right_logical x y shifts x to the right
by y bits.
This is a logical shift: zeroes are inserted in the vacated bits
regardless of the sign of x.
The result is unspecified if y < 0 or y >= bitsize.
val of_int : 'a int -> 'a nativeint
Convert the given integer (type
int) to a native integer
(type nativeint).
val to_int : 'a nativeint -> 'a int
Convert the given native integer (type
nativeint) to an
integer (type int). The high-order bit is lost during
the conversion.
val of_float : 'a float -> 'a nativeint
Convert the given floating-point number to a native integer,
discarding the fractional part (truncate towards 0).
The result of the conversion is undefined if, after truncation,
the number is outside the range
[
Nativeint.min_int, Nativeint.max_int].
val to_float : 'a nativeint -> 'a float
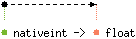
Convert the given native integer to a floating-point number.
val of_int32 : 'a int32 -> 'a nativeint
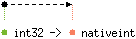
Convert the given 32-bit integer (type
int32)
to a native integer.
val to_int32 : 'a nativeint -> 'a int32
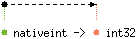
Convert the given native integer to a
32-bit integer (type
int32). On 64-bit platforms,
the 64-bit native integer is taken modulo 232,
i.e. the top 32 bits are lost. On 32-bit platforms,
the conversion is exact.
val of_string : 'a string -{'b | Failure: 'b |}-> 'a nativeint
with 'a < 'b
with 'a < 'b
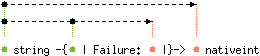
Convert the given string to a native integer.
The string is read in decimal (by default) or in hexadecimal,
octal or binary if the string begins with
0x, 0o or 0b
respectively.
Raise Failure "int_of_string" if the given string is not
a valid representation of an integer.
val to_string : 'a nativeint -> 'a string
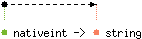
Return the string representation of its argument, in decimal.
type (#'a:level) t = 'a nativeint
An alias for the type of native integers.
val compare : 'a t -> 'a t -> 'a int
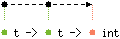
The comparison function for native integers, with the same specification as
Pervasives.compare. Along with the type t, this function compare
allows the module Nativeint to be passed as argument to the functors
Set.Make and Map.Make.

This module provides operations on the type
nativeintof signed 32-bit integers (on 32-bit platforms) or signed 64-bit integers (on 64-bit platforms). This integer type has exactly the same width as that of alonginteger type in the C compiler. All arithmetic operations overnativeintare taken modulo 232 or 264 depending on the word size of the architecture.Performance notice: values of type
nativeintoccupy more memory space than values of typeint, and arithmetic operations onnativeintare generally slower than those onint. Usenativeintonly when the application requires the extra bit of precision over theinttype.