Generic interface
type (='a:type, ='b:type, ='c:level, #'d:level) t
The type of hash tables from type
'a to type 'b.
val create : 'a int -> ('b, 'c, 'a, 'd) t
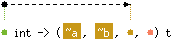
Hashtbl.create n creates a new, empty hash table, with
initial size n. For best results, n should be on the
order of the expected number of elements that will be in
the table. The table grows as needed, so n is just an
initial guess.
val clear : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'c) t -{'c ||}-> unit
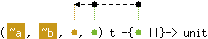
Empty a hash table.
val add : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'c) t -> 'd -> 'b -{'c ||}-> unit
with 'd < 'a
and content('a), content('d) < 'c
with 'd < 'a
and content('a), content('d) < 'c
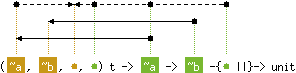
Hashtbl.add tbl x y adds a binding of x to y in table tbl.
Previous bindings for x are not removed, but simply
hidden. That is, after performing Hashtbl.remove tbl x,
the previous binding for x, if any, is restored.
(Same behavior as with association lists.)
val copy : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'd) t -> ('e, 'f, 'd, 'g) t
with 'a < 'e
and 'b < 'f
and 'c < 'd
with 'a < 'e
and 'b < 'f
and 'c < 'd
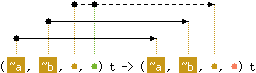
Return a copy of the given hashtable.
val find : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'd) t -> 'e -{'f | Not_found: 'f |}-> 'g
with 'e ~ 'a
and content('a), 'c, 'd, content('e) < level('g)
and 'b < 'g
and content('a), 'c, 'd, content('e) < 'f
with 'e ~ 'a
and content('a), 'c, 'd, content('e) < level('g)
and 'b < 'g
and content('a), 'c, 'd, content('e) < 'f
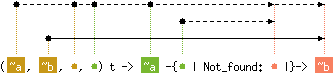
Hashtbl.find tbl x returns the current binding of x in tbl,
or raises Not_found if no such binding exists.
val find_all : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'd) t -> 'e -> ('b, 'd) list
with 'a ~ 'e
and content('a), 'c, content('e) < 'd
with 'a ~ 'e
and content('a), 'c, content('e) < 'd
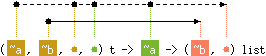
Hashtbl.find_all tbl x returns the list of all data
associated with x in tbl.
The current binding is returned first, then the previous
bindings, in reverse order of introduction in the table.
val mem : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'd) t -> 'e -> 'd bool
with 'a ~ 'e
and content('a), 'c, content('e) < 'd
with 'a ~ 'e
and content('a), 'c, content('e) < 'd
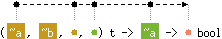
Hashtbl.mem tbl x checks if x is bound in tbl.
val remove : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'c) t -> 'd -{'c ||}-> unit
with 'a ~ 'd
and content('a), content('d) < 'c
with 'a ~ 'd
and content('a), content('d) < 'c

Hashtbl.remove tbl x removes the current binding of x in tbl,
restoring the previous binding if it exists.
It does nothing if x is not bound in tbl.
val replace : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'c) t -> 'd -> 'b -{'c ||}-> unit
with 'd < 'a
and content('a), content('d) < 'c
with 'd < 'a
and content('a), content('d) < 'c
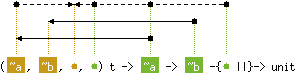
Hashtbl.replace tbl x y replaces the current binding of x
in tbl by a binding of x to y. If x is unbound in tbl,
a binding of x to y is added to tbl.
This is functionally equivalent to Hashtbl.remove tbl x
followed by Hashtbl.add tbl x y.
val iter : ('a -{'b | 'c | 'd}-> 'e -{'f | 'c | 'f}-> 'g) ->
('a, 'e, 'h, 'd) t -{'d | 'c |}-> unit
with content('c), 'd, 'h < 'f
and content('c), 'd, 'h < 'b
('a, 'e, 'h, 'd) t -{'d | 'c |}-> unit
with content('c), 'd, 'h < 'f
and content('c), 'd, 'h < 'b
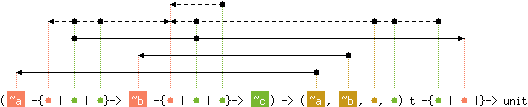
Hashtbl.iter f tbl applies f to all bindings in table tbl.
f receives the key as first argument, and the associated value
as second argument. The order in which the bindings are passed to
f is unspecified. Each binding is presented exactly once
to f.
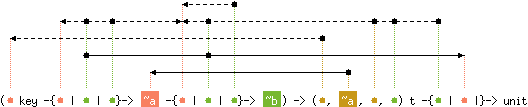
val fold : ('a -{'b | 'c | 'd}-> 'e -{'f | 'c | 'g}-> 'h -{'i | 'c | 'j}-> 'h) ->
('a, 'e, 'k, 'd) t -> 'h -{'d | 'c |}-> 'h
with content('c), 'd, 'g, 'j, 'k < 'i
and content('c), 'd, 'g, 'k < 'f
and content('c), 'd, 'k < 'b
and content('c), 'd, 'g, 'j, 'k < level('h)
('a, 'e, 'k, 'd) t -> 'h -{'d | 'c |}-> 'h
with content('c), 'd, 'g, 'j, 'k < 'i
and content('c), 'd, 'g, 'k < 'f
and content('c), 'd, 'k < 'b
and content('c), 'd, 'g, 'j, 'k < level('h)
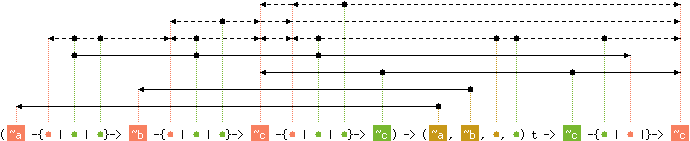
Hashtbl.fold f tbl init computes
(f kN dN ... (f k1 d1 init)...),
where k1 ... kN are the keys of all bindings in tbl,
and d1 ... dN are the associated values.
The order in which the bindings are passed to
f is unspecified. Each binding is presented exactly once
to f.
Module type HashedType
The input signature of the functor
Hashtbl.Make.
module type HashedType = sig
type (#'a:level) t
The type of the hashtable keys.
val equal : 'a t -> 'a t -> 'a bool
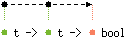
The equality predicate used to compare keys.
val hash : 'a t -> 'a int
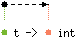
A hashing function on keys. It must be such that if two keys are
equal according to
equal, then they have identical hash values
as computed by hash.
Examples: suitable (equal, hash) pairs for arbitrary key
types include
((=), Hashtbl.hash) for comparing objects by structure, and
((==), Hashtbl.hash) for comparing objects by addresses
(e.g. for mutable or cyclic keys).
end
Module type S
The output signature of the functor
Hashtbl.Make.
module type S = sig
type (#'a:level) key
type (='a:level, ='b:type, ='c:level, #'d:level) t
val create : 'a int -> ('b, 'c, 'a, 'd) t
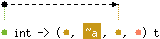
val clear : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'c) t -{'c ||}-> unit
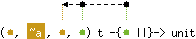
val copy : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'd) t -> ('e, 'f, 'd, 'g) t
with 'c < 'd
and 'a < 'e
and 'b < 'f
with 'c < 'd
and 'a < 'e
and 'b < 'f
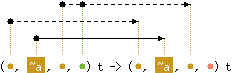
val add : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'c) t -> 'a key -> 'b -{'c ||}-> unit
with 'a < 'c
with 'a < 'c
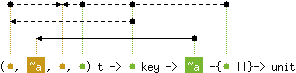
val remove : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'c) t -> 'c key -{'c ||}-> unit
with 'a < 'c
with 'a < 'c
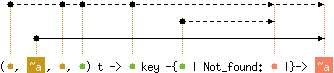
val find : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'd) t -> 'd key -{'e | Not_found: 'e |}-> 'f
with 'a, 'c, 'd < 'e
and 'a, 'c, 'd < level('f)
and 'b < 'f
with 'a, 'c, 'd < 'e
and 'a, 'c, 'd < level('f)
and 'b < 'f
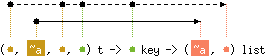
val find_all : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'd) t -> 'd key -> ('b, 'd) list
with 'a, 'c < 'd
with 'a, 'c < 'd
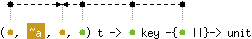
val replace : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'c) t -> 'a key -> 'b -{'c ||}-> unit
with 'a < 'c
with 'a < 'c
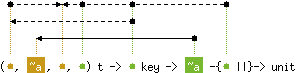
val mem : ('a, 'b, 'c, 'd) t -> 'd key -> 'd bool
with 'a, 'c < 'd
with 'a, 'c < 'd

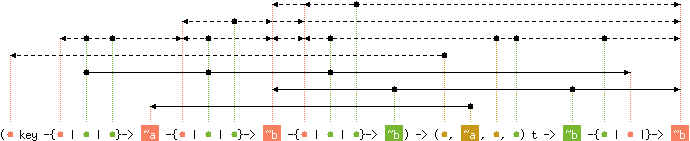
val iter : ('a key -{'b | 'c | 'd}-> 'e -{'f | 'c | 'f}-> 'g) ->
('a, 'e, 'h, 'd) t -{'d | 'c |}-> unit
with content('c), 'd, 'h < 'f
and content('c), 'd, 'h < 'b
('a, 'e, 'h, 'd) t -{'d | 'c |}-> unit
with content('c), 'd, 'h < 'f
and content('c), 'd, 'h < 'b
val fold : ('a key -{'b | 'c | 'd}->
'e -{'f | 'c | 'g}-> 'h -{'i | 'c | 'j}-> 'h) ->
('a, 'e, 'k, 'd) t -> 'h -{'d | 'c |}-> 'h
with content('c), 'd, 'g, 'j, 'k < 'i
and content('c), 'd, 'g, 'k < 'f
and content('c), 'd, 'k < 'b
and content('c), 'd, 'g, 'j, 'k < level('h)
'e -{'f | 'c | 'g}-> 'h -{'i | 'c | 'j}-> 'h) ->
('a, 'e, 'k, 'd) t -> 'h -{'d | 'c |}-> 'h
with content('c), 'd, 'g, 'j, 'k < 'i
and content('c), 'd, 'g, 'k < 'f
and content('c), 'd, 'k < 'b
and content('c), 'd, 'g, 'j, 'k < level('h)
end
module Make : functor (H : HashedType) -> S with type 'a key = 'a H.t
Functor building an implementation of the hashtable structure.
The operations perform similarly to those of the generic
interface, but use the hashing and equality functions
specified in the functor argument
H instead of generic
equality and hashing.
The polymorphic hash primitive
val hash : 'a -> 'b int
with content('a) < 'b
with content('a) < 'b
Hashtbl.hash x associates a positive integer to any value of
any type. It is guaranteed that
if x = y, then hash x = hash y.
Moreover, hash always terminates, even on cyclic
structures.
val hash_param : 'a int -> 'a int -> 'b -> 'a int
with content('b) < 'a
with content('b) < 'a

Hashtbl.hash_param n m x computes a hash value for x, with the
same properties as for hash. The two extra parameters n and
m give more precise control over hashing. Hashing performs a
depth-first, right-to-left traversal of the structure x, stopping
after n meaningful nodes were encountered, or m nodes,
meaningful or not, were encountered. Meaningful nodes are: integers;
floating-point numbers; strings; characters; booleans; and constant
constructors. Larger values of m and n means that more
nodes are taken into account to compute the final hash
value, and therefore collisions are less likely to happen.
However, hashing takes longer. The parameters m and n
govern the tradeoff between accuracy and speed.

Hash tables are hashed association tables, with in-place modification.